USB HUB Types: Never Run Out Of USB Slots Again!

A USB hub is a device that expands a single USB port into multiple USB ports. It allows you to connect and use multiple USB devices through a single USB port on your computer. USB hubs come in different types to suit different needs and devices.
The main types of USB hubs available are USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB-C, powered, USB 3.1 Gen 2, and wireless USB hubs. Each type has its own advantages and suitability for different devices. Now, let's explore all these types n detail;
① USB 2.0 Hub
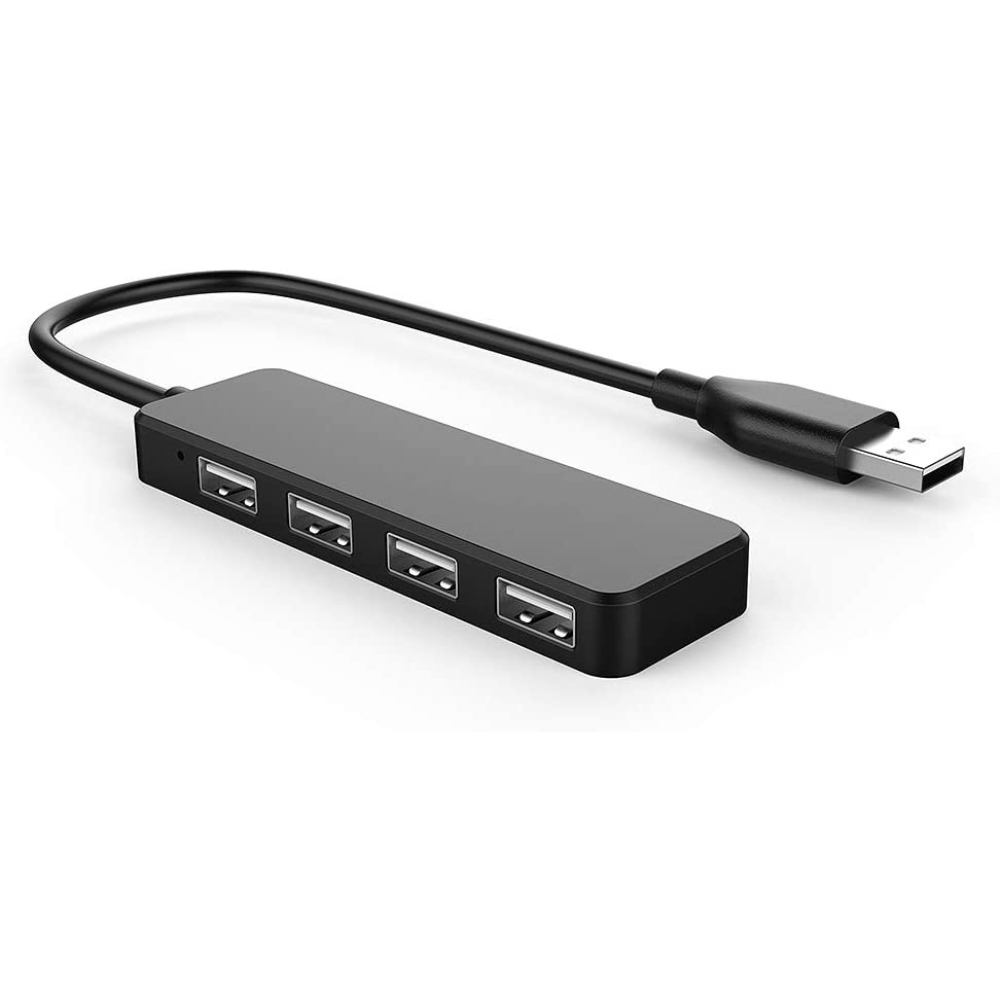

The USB 2.0 hub is the most common and widely used type. It provides a maximum transfer speed of up to 480 Mbps, making it suitable for connecting a wide range of USB 2.0 and 1.1 devices like keyboards, mice, printers, and external storage devices. Its pros include backward compatibility with older USB standards, affordability, and wide availability. The USB 2.0 hub is an excellent choice for basic connectivity needs and home use where fast data transfer rates are not critical. Additionally, it is suitable for users with older devices that are not compatible with faster USB standards. However, it lacks the faster speeds of newer USB standards, limiting its capabilities for data-intensive tasks.
② USB 3.0 Hub:
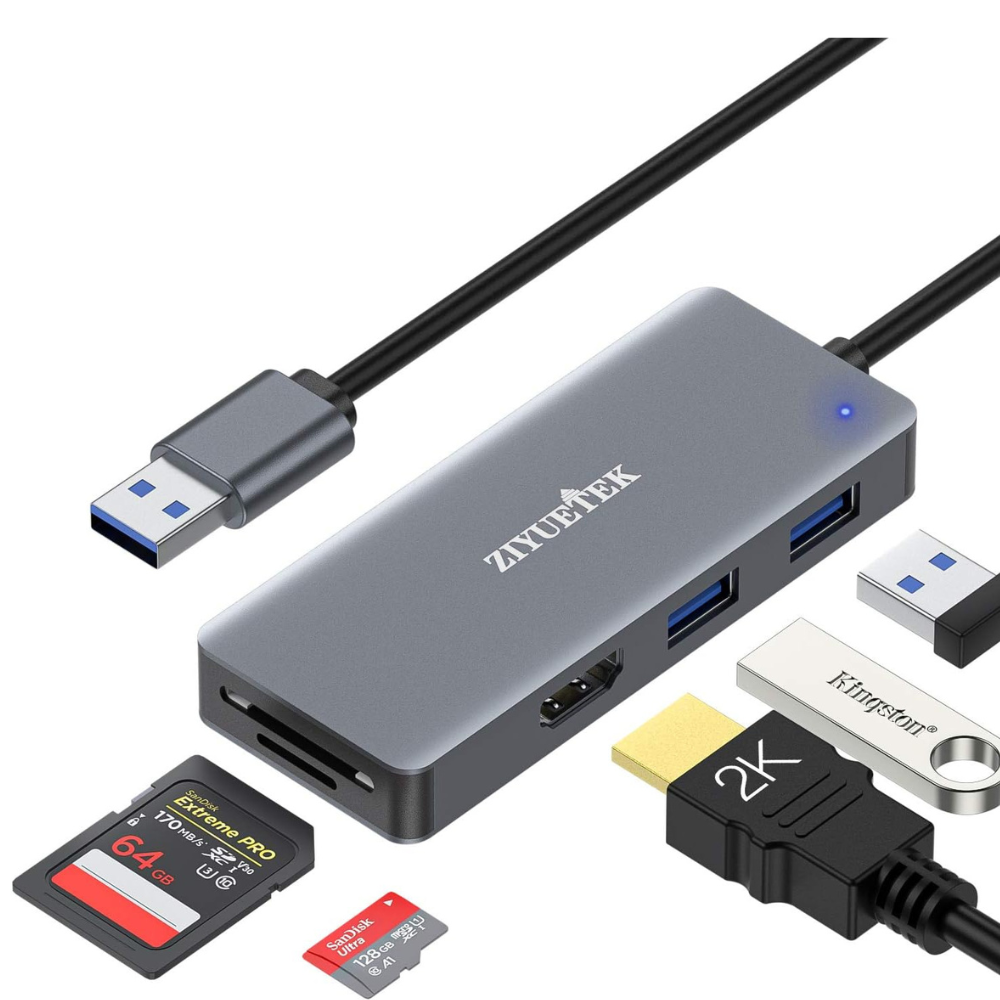

The USB 3.0 hub boasts faster transfer speeds of up to 5 Gbps, making it ideal for data-intensive tasks such as transferring large files or streaming high-definition videos. It is compatible with USB 2.0, 1.1 devices, but truly shines when used with USB 3.0 devices. The advantages of USB 3.0 hubs include improved data transfer rates, enhanced power management, and faster charging capabilities for compatible devices. Additionally, USB 3.0 hubs incorporate backward compatibility, allowing users to connect their existing USB devices seamlessly. It is worth mentioning that a USB 3.0 hub may require driver installation for full functionality, which can be a drawback for some users.
③ USB-C Hub:
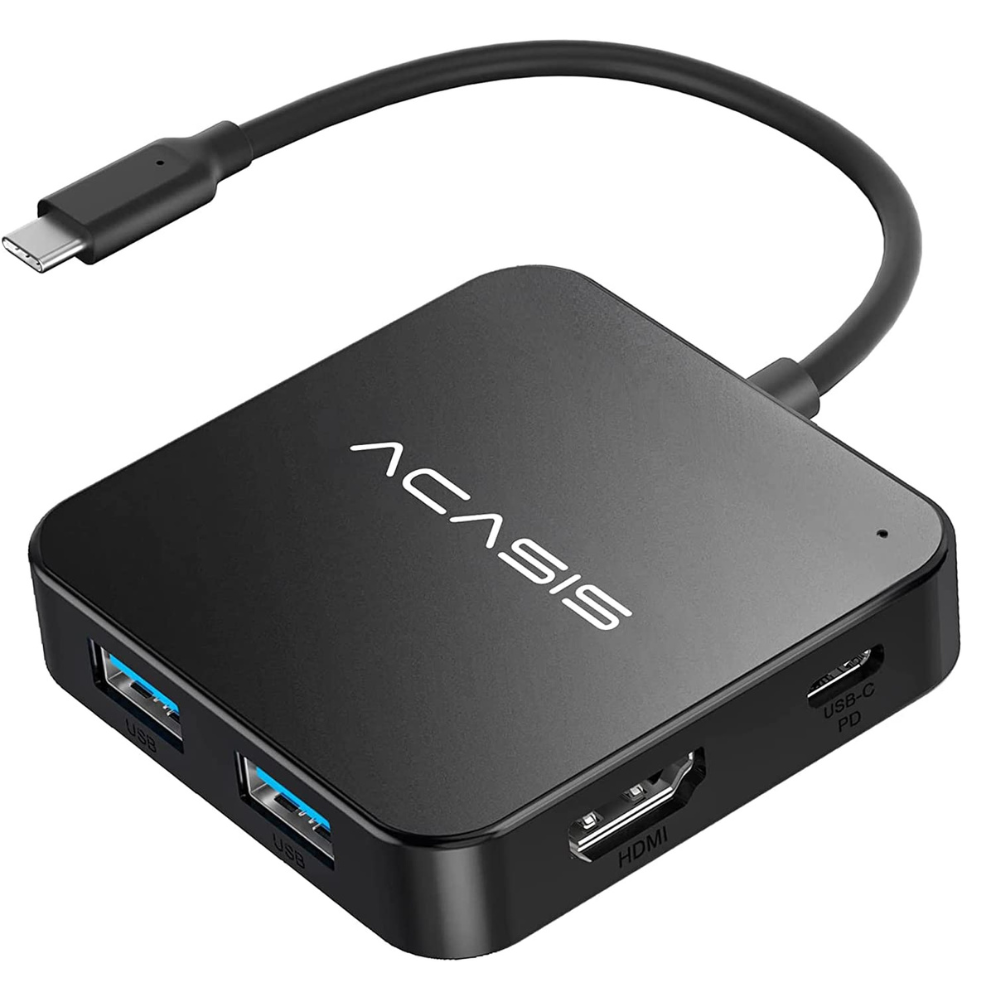

The USB-C hub utilizes the versatile USB Type-C connector, allowing for higher transfer speeds and power delivery compared to USB 2.0 and 3.0 hubs. It offers seamless compatibility with USB-C devices like MacBooks, Chromebooks, and smartphones. Users benefit from the reversible connector, which means no more frustrating attempts to connect the cable the right way up. The USB-C hub provides benefits such as fast data transfers, simultaneous charging of connected devices, and support for various peripherals like external monitors and storage devices. However, while USB-C is becoming increasingly prevalent, some devices still lack USB-C ports, which may require the use of adapters and reduce the conveniences of this hub type.
④ Powered USB Hub:
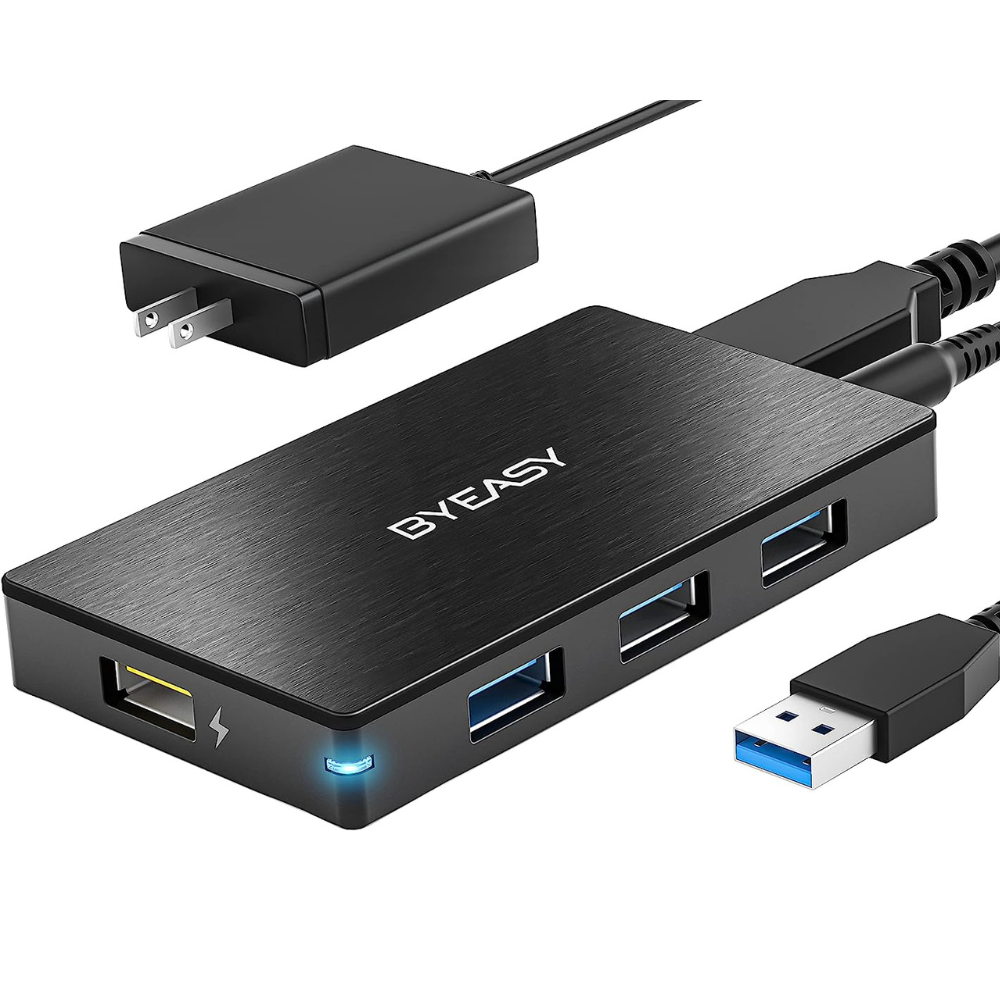

A powered USB hub comes with an external power adapter, providing additional power to connected devices. This type of hub is ideal for power-hungry peripherals like external hard drives, multiple high-speed monitors, and other energy-intensive devices. Powered USB hubs bring benefits such as increased power output, stable device performance, and better device charging capabilities. Furthermore, they can eliminate the issue of insufficient power supply from the computer itself. However, it is important to note that using a powered USB hub requires an available power outlet, which may add to the clutter especially if multiple hubs are needed, and limits the portability of the hub.
⑤ USB 3.1 Gen 2 Hub:
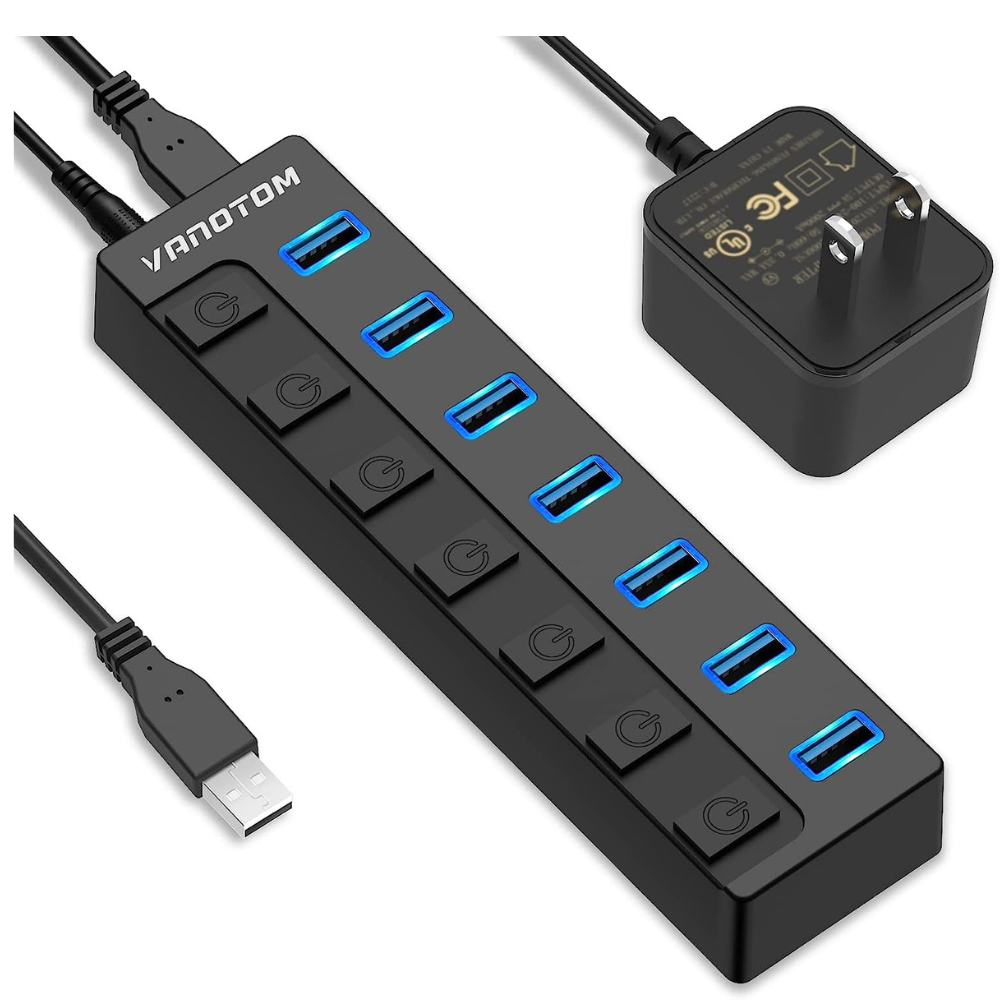

The USB 3.1 Gen 2 hub caters to users seeking the highest data transfer rates available, capable of reaching up to 10 Gbps. It is compatible with USB 3.1 Gen 2 devices, enabling lightning-fast transfers and improved performance for demanding applications such as video editing or accessing large files stored on external drives. The advantages of USB 3.1 Gen 2 hubs include future-proofing, reduced data transfer times, and enhanced connectivity options. However, it is essential to consider that USB 3.1 Gen 2 hubs may be costlier compared to other USB hub types, and their full potential is only realized when paired with compatible devices.
⑥ Wireless USB Hub:
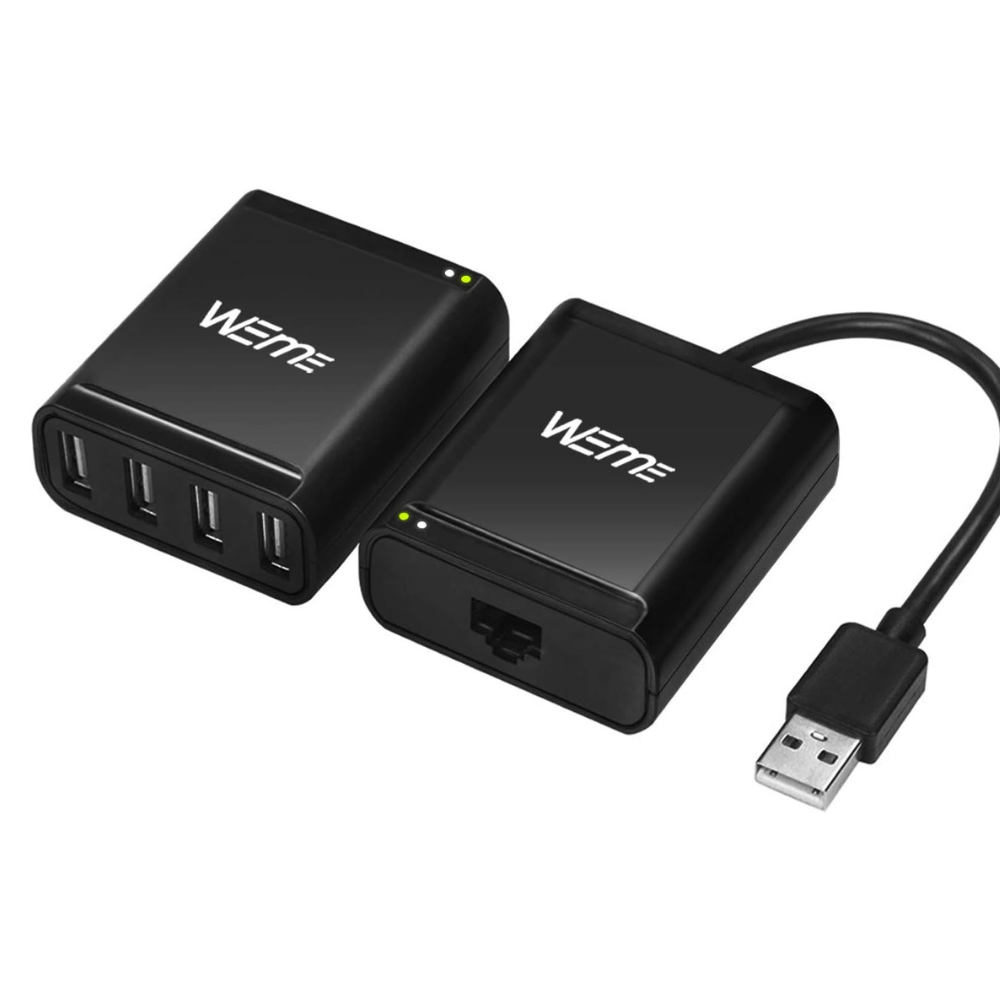

Wireless USB hubs eliminate the need for physical USB cables, offering greater flexibility and convenience in connecting devices. This type of hub works well for situations where cables are impractical or result in a cluttered workspace. Users benefit from wireless connectivity, reduced cable mess, and easy device mobility. Wireless USB hubs are particularly advantageous for connecting peripherals like keyboards, mice, scanners, and printers, as they allow for more convenient placement without the usual cable limitations. However, wireless connectivity may have limited range and can be susceptible to potential interference from other wireless devices, which may affect signal stability and transfer speeds compared to wired alternatives.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a USB Hub
In today's technology-driven world, USB hubs have become an essential accessory for many individuals. With the increasing number of devices that require USB connections, choosing the right USB hub is crucial. However, with the wide range of options available in the market, it can be overwhelming to make a decision. To help you in this process, we have outlined five key factors to consider when choosing a USB hub.
➛ Number of Ports:
The number of ports on a USB hub is one of the first factors to consider. Determine how many devices you need to connect simultaneously and ensure that the USB hub you choose has enough ports to accommodate them. It is always a good idea to have a few extra ports for future expansion. Additionally, consider the type of ports available, such as USB 2.0, USB 3.0, or USB-C, depending on the devices you plan to connect.
➛ Power Requirements:
Another crucial factor to consider is the power requirements of your devices. Some USB hubs are bus-powered, meaning they draw power directly from the connected device. If you have power-hungry devices like external hard drives or high-speed charging smartphones, it is advisable to opt for a USB hub with an external power supply. This ensures that all your devices receive sufficient power without draining the battery life of your computer or laptop.
➛ Data Transfer Speed:
Data transfer speed is an important consideration, especially if you frequently transfer large files or work with data-intensive applications. USB 2.0 hubs offer a maximum transfer speed of 480 Mbps, while USB 3.0 and USB 3.1 hubs provide significantly faster speeds of up to 5 Gbps and 10 Gbps, respectively. Choose a USB hub that supports the highest data transfer speed your devices are compatible with to ensure efficient and speedy file transfers.
➛ Compatibility with Devices:
Before making a purchase, ensure that the USB hub you choose is compatible with your devices. Some USB hubs may have limitations with operating systems or specific devices. Check the product specifications to confirm compatibility with your computer, laptop, or other devices. Additionally, consider any future devices you may acquire and ensure the USB hub has the necessary compatibility for future-proofing your setup.
➛ Build Quality and Design:
Lastly, consider the build quality and design of the USB hub. Look for hubs made from durable materials that can withstand daily use and potential travel. A compact and lightweight design can be beneficial if you often need to carry your USB hub with you. Additionally, consider the placement and spacing of the ports to ensure easy access and prevent overcrowding. A well-designed USB hub can enhance your overall user experience and seamlessly integrate into your workspace.
Conclusion:
In summary, USB hubs are invaluable tools for expanding USB connectivity options. The choice of USB hub type depends on factors such as transfer speed requirements, compatibility, power needs, and convenience. For users seeking affordable options with backward compatibility, USB 2.0 hubs are suitable. If faster transfer speeds are crucial, USB 3.0 and USB 3.1 Gen 2 hubs are recommended. Those looking for versatile connectivity with USB-C devices should opt for USB-C hubs. Powered USB hubs cater to power-demanding peripherals, while wireless USB hubs provide cable-free convenience.
Whether you require a basic setup or a high-performance hub, there are various options available to suit your specific needs. Assess your requirements carefully to select the most suitable USB hub type that will enhance your user experience. USB hubs have become an indispensable accessory in our increasingly connected world, and choosing the right one can significantly improve efficiency and productivity.